
There has been rising concern about genetic polymorphism because of the disabilities and life-long health issues associated with them. Among the many gene variants, MTHFR – a gene responsible for regulating homocysteine levels and folate – has been reported to have no frank symptoms in people who carry its variant, however, we beg to differ.
MTHFR stands for methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, an enzyme which is associated with many important bodily functions. Homocysteine is an amino acid, which is broken down to methionine by the MTHFR enzyme. The production of this enzyme is regulated by the MTHFR gene. In the presence of polymorphisms, either C677T or A1289C, this enzyme is reduced in its ability to create active folate by up to 75%. As a result, homocysteine levels may rise in the body and the folate level decreases. A polymorphic MTHFR gene may also result in systemic defects associated with your ability to have a successful pregnancy.
For example:
– Issues in the reproductive tract,
– Miscarriage
– Sperm production
– Egg production
– Blood-clotting mechanisms,
– Midline defects in the foetus like: spina bifida, cleft lip, cleft palate etc.
– Not everyone is affected the same way and our environment has a big part to play in how our genes are expressed. For example, the more stressed you are, the more likely you are to have issues associated with the MTHFR gene variant. This is because the methyl groups that you need for fertility are used up in stress.
So, how can one suspect whether an MTHFR mutation is present?
Elevated homocysteine levels (15 μmol/L) and a deficiency of folate have been found to be associated with several symptoms. Let’s elaborate on what these symptoms are and how they can affect pregnancy. (1)
Blood clotting disorders
Studies have found that high homocysteine levels can be harmful to the inner lining cells of the blood vessels. Damaged blood vessels trigger healing response and blood clots are formed in the areas of such damage – a condition called thrombosis. Due to persistently high homocysteine levels, these clots continue to develop and may even block the arteries in different areas of the body.
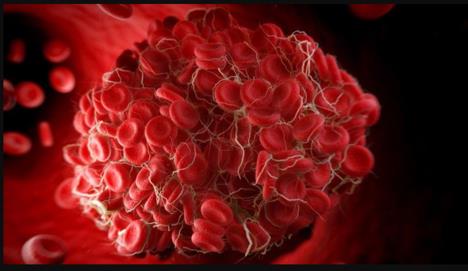

How does a blood clotting disorder affect pregnancy?
If you carry an MTHFR gene variant, chances are high that these abnormal clots may form in the placenta. As a result, the blood supply to the foetus is cut off, which can further lead to stillbirth. If the clot is large enough, it can disrupt the placenta completely and lead to a miscarriage. Many research studies have shown a positive association between high homocysteine levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes including thrombosis,miscarriages, recurrent implantation failure, and placental disruption.
Anaemia
Periodic rejuvenation of body cells and tissues is a necessity for optimal functioning of the body. For this, all the cells in the body undergo cell division to generate new and efficient cells and discard the old and dying ones. A similar process occurs in the blood cells as well. However, an MTHFR polymorphism makes it difficult for the body to produce these cells leading to anaemia. If you’re experiencing fatigue, tiredness, loss of appetite and paleness of the skin, you may have anaemia. (2)

How does anaemia affect pregnancy?
Due to a lack of folate and presence of MTHFR variant, red blood cell production is affected in the mother’s body. As a result, when you’re pregnant, the baby doesn’t get enough haemoglobin and oxygen from your body for optimal growth. Studies have found that children born to anaemic mothers are delivered before full term and have low birth weight. It has also been reported that difficult labour, postpartum haemorrhage and stillbirths are also associated with anaemia during pregnancy. (3)
Developmental defects
Methionine is an essential amino acid that provides methyl groups for DNA and RNA production. However, the MTHFR gene variation disturbs folate production and conversion of homocysteine to methionine. When this happens, abnormal and low-quality cell production occurs in the foetus which results in developmental defects.
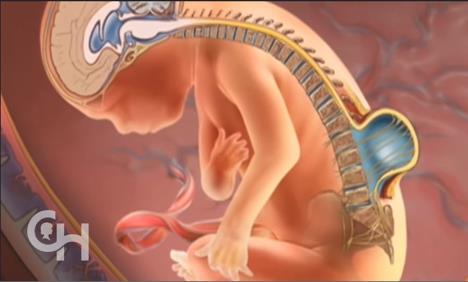

How does a developmental affect pregnancy?
Research says that folate deficiency and MTHFR polymorphism is associated with incomplete enclosure of the developing nerves and spinal cord by the spinal bones, which causes neural tube defects. (4) This is where a gap develops in the spine and the condition is known as spina bifida. (5) Not only this but MTHFR has also been reported to be associated with Down syndrome and restricted foetal growth in the uterus. (6), (7)
Preeclampsia
Research studies have shown that an elevated homocysteine level is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease. (8) The presence of an MTHFR gene variant my put you at higher risk of blood vessel wall damage and stiffening. Due to this stiffening, these blood vessels lose their elasticity to regulate and maintain blood pressure within the normal range. This causes an expecting mother to have high blood pressure, which is seen in preeclampsia.


How does preeclampsia affect pregnancy?
Preeclampsia is a serious medical condition, which is characterised by high blood pressure, protein excretion in the urine and swelling in the body. This condition may worsen with time and progress to eclampsia wherein the mother may suffer from red blood cell destruction, abnormal blood clot formation and seizures. It has been reported that preeclampsia affects around 3-8% of pregnant women and may cause retarded foetal growth or miscarriage. (9), (10), (11)
Mental health problems
Good mental health is as important for a successful pregnancy as is good physical health. Research says that reduced MTHFR enzymatic activity and folate deficiency are associated with an increased risk of mental health problems, such as depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and so on. (12)
How does a mental health problem affect pregnancy?
Studies have found that women with mental health problems deliver before reaching full term as compared to those who have no mental health issues. Also, it has been reported that children born to women with mental health problems are of low birth weight. Giving birth to a low-weight baby has been found to be associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. (13)
Conclusion
MTHFR polymorphisms don’t cause any symptoms per se, however, the side effects of low folate are many. The more stressed you are, the more the MTHFR enzyme is likely to express and cause a lower folate level. This may manifest itself in anxiety, depression, fatigue, fat metabolism issues, multiple chemical sensitivity, infertility just to name a few. It is usually identified following a genetic test when there is no other explanation for the symptoms mentioned above in a person. So if you think you or your partner may have the MTHFR gene variant, then testing is simple. The end result is that you can do something about low folate levels which will improve your overall health and your chances of falling pregnant. To know more, read our blog on how MTHFR can affect your fertility and pregnancy.
1. Take our Quiz to see if you might have the MTHFR gene.
2. How to test for the MTHFR gene.
References
- MTHFR Gene. Medline Plus, US National Library of Medicine. Viewed 2021.
- Greenberg JA, et al. Folic Acid supplementation and pregnancy: more than just neural tube defect prevention. Rev Obstet Gynecol. 2011;4(2):52-59.
- Suryanarayana R, et al. Prospective study on prevalence of anemia of pregnant women and its outcome: A community based study. J Family Med Prim Care. 2017;6(4):739-743.
- Laanpere M, et al. Folate-metabolizing gene variants and pregnancy outcome of IVF. Reprod Biomed Online. 2011 Jun;22(6):603-14.
- Spina Bifida. Medline Plus, US National Library of Medicine. Viewed 2021.
- Zhang Y, et al. The association between maternal methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T and A1298C polymorphism and birth defects and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Prenat Diagn. 2019 Jan;39(1):3-9.
- Paul S, et al. Association of FOLH1, DHFR, and MTHFR gene polymorphisms with susceptibility of Neural Tube Defects: A case control study from Eastern India. Birth Defects Res. 2018 Aug 15;110(14):1129-1138.
- Parra-Pingel PE, et al. Pregnancy outcomes in younger and older adolescent mothers with severe preeclampsia. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2017;8:81-86.
- Parra-Pingel PE, et al. Pregnancy outcomes in younger and older adolescent mothers with severe preeclampsia. Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2017;8:81-86.
- Wu X, et al. Folate metabolism gene polymorphisms MTHFR C677T and A1298C and risk for preeclampsia: a meta-analysis. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2015;32(5):797-805.
- Hansen AT, et al. The genetic component of preeclampsia: A whole-exome sequencing study. PLoS One. 2018;13(5):e0197217.
- Wan L, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase and psychiatric diseases. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):242.
- Hironaka M, et al. Maternal mental disorders and pregnancy outcomes: a clinical study in a Japanese population. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2011 Oct;37(10):1283-9.
